
For lot of applications, the critical parameters such as temperature, humidity, pressure etc. need to be monitored and recorded in real time preferably with an alert system to generate alerts in case the parameters exceed the permitted levels. These are generally known as real time monitoring systems. Temperature is the most common parameter being monitored and hence is commonly referred as remote temperature monitoring.
Applications of real time monitoring systems
Few of the major applications which require real time monitoring system are listed below:
Temperature monitoring for refrigerators which are used to keep medicines, vaccines etc. (certain customers also need temperature & humidity monitoring)
Temperature & Humidity monitoring of warehouses which are used to store temperature sensitive products such as medicine, chemicals, food, fruits & vegetables etc.
Temperature & humidity monitoring of walk in freezers, cold rooms, cold storages etc. which are used to store vaccines, medicines, frozen food etc.
Temperature monitoring of industrial freezers
Monitoring of Temperature, humidity, engine conditions etc. for vehicles, reefers etc. which transport temperature sensitive goods.
Temperature Monitoring along with humidity, water leakage etc. for data centers and server rooms. Temperature monitoring is very critical for server rooms since server panels generate lot of heat.
Monitoring of temperature, humidity and pressure for patient rooms, Intensive care units, clean rooms, clinically isolated rooms etc. in hospitals.
Temperature, humidity and pressure monitoring in clean rooms in manufacturing environments.
Temperature monitoring of furnaces, kilns, autoclaves, industrial equipment, processing machines etc.
Temperature monitoring during concrete curing process.
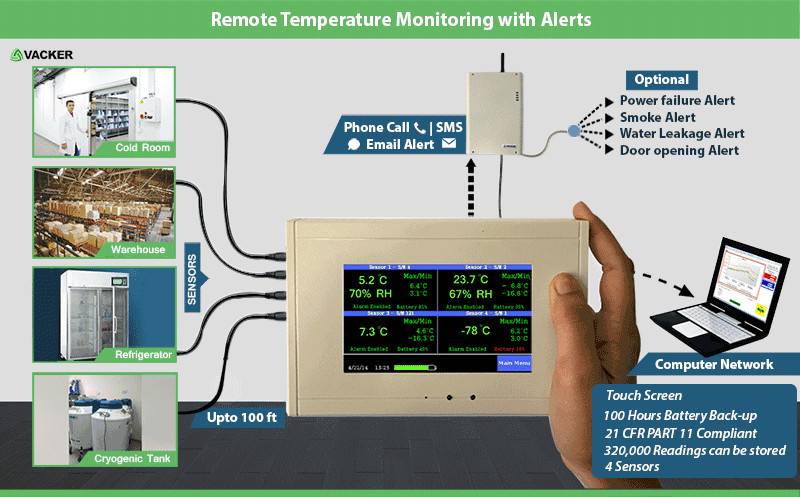

Operating principle of real time monitoring system

The basic principle of all such systems involve lot of sensors such as temperature sensor, humidity sensor, pressure sensor etc. These sensors continuously collect data at preprogrammed intervals known as sampling interval. The sampling interval can vary from micro seconds to hours based on the criticality of the parameter being monitored. All the sensors continuously communicate the collected data to a central base station. The mode of communication from the sensors to the base station can be in different modes as explained in the next article. This base station transmits the collected data to the internet. Also, this base station continuously analyzes the data for any alerts. If any of the parameters exceed the preprogrammed alert levels, alerts such as email, SMS, voice call etc. will be generated to the operators.

Our solution for monitoring of refrigerators & freezers
We are providing a complete solution for monitoring of refrigerators and freezers. Major features are:
Integrated with Temperature and Humidity Data Loggers which can record months of data continuously.
Sensors which can go into any part of the refrigerator and extendable up to 25 meters
Up to 4 refrigerators or freezers can be connected in same remote monitoring system
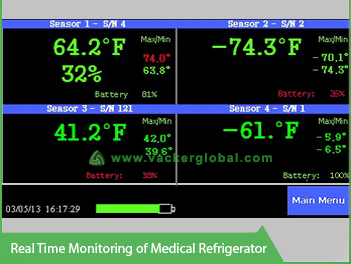
Current readings of temperature and humidity of the refrigerator will be displayed in the local screen.
Phone call, SMS & Email alert systems if temperature or humidity of the refrigerator goes above limits
Also door opening monitoring of the refrigerator can be provided separately.
Data can be recorded in the monitoring system as well as over Local Area Network.
Different models which can work on WiFi, radio frequency or Ethernet system
Compliant to 21CFR Part 11 in accordance with US standards
Free software for remote refrigerator monitoring
100 hour battery backup so that data will not be lost in case of power failure


Technical specification
Brief technical specification of the remote refrigerator monitoring system and software are as below:
Data logger capable of storing 80,000 readings.
4 temperature sensors or 4 temperature & humidity sensors can be connected to a single device
Temperature range from -200°C to 1350°C (different types of thermocouples)
Type of alerts : Low temperature, High temperature, delay timer for each alert
Type of screen : touch screen LCD, size 6.35 cm x 11.43 cm
Alerts : Email, SMS & phone call through an external dialer
Size of the monitor (cm) : 22 x 12.7 x 3.5
Type of sensors: Wireless and Wired sensors. Wireless sensors operate on radio frequency of 433 MHz
Sampling interval: programmable from 1 minute to 24 hours
PC Software : free of charge
Local network software with email alerts : one time optional fee
Weight of the monitoring screen device without the sensors : 510 gms


Types of real time remote temperature monitoring systems
Based on the technology of the device there are different types of monitoring systems as explained below:
- Ethernet-based real-time monitoring systems
The sensors are connected to an Ethernet system through CAT6 cables and connectors, just similar to connecting a computer, printer etc. You will need to have Ethernet ports near to each sensor. These can be powered from an electrical plug or can be POE type (Power over Ethernet). There will not be a separate base station, but a computer in the network can act as the base station.
- WiFi communication based real time remote temperature monitoring system
Here there is no Ethernet cabling required. The communication between the sensor and the central station takes place through WiFi routers used for connecting all other computers. The WiFi communication needs power and if you need continuous data transmission, you may have to go for sensors which are powered through an AC supply. There are devices available which continuously collect data and stores in itself and transmits the data only once or twice in a day. Such systems can work on its own battery for a long duration since it is connecting to WiFi only once or twice in a day.

In this case also there will not be a separate base station, but a computer in the network can act as the base station. The communication reliability depends on the strength and range of the WiFi router.
- Radio Frequency based real-time remote temperature monitoring system
These work on Radio frequency. While selecting a device you have to check that the device works on the radio frequency approved by the local authorities. The supplier has to take approval for the device from the authorities. These devices have a comparatively long range of communication from the base station. The base station acts as a receiver and the sensors act as transmitters. There will be continuous interaction between the sensors and the base station.
Such sensor operates with a very low power requirement and hence can have a long battery life without supporting power supply.
- Zigbee protocol based real time monitoring system
Zigbee is the latest technology with a direct range of up to 1 km in air. If there are obstructions in its path, the range comes down accordingly. Zigbee operates in a permitted frequency range in most of the countries. Zigbee sensors also operate on very low power requirement and hence can operate without electric power.
- IP sensor-based real-time monitoring systems
These might be the most economical type of monitoring system. Each sensor has to be connected to an Ethernet port and does not require electric power. These operate on POE (Power Over Ethernet) Also this may not have its own memory. There will be a central software in one of the PCs or server in your Ethernet system. Each sensor can be configured to this software. The sensor is simply inserted into an Ethernet port and it starts working.

Comparison of different technologies of real time monitoring systems
| Parameter | Ethernet | Wifi | RF | Zigbee | IP Sensors |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Operating frequency/protocol | Computer Network | 802.11a/b/g/n/n-draft | Varies for each country | 802.15.4 | Computer Network |
| Flexibility to move sensors | Limited to the length of wire | 20-30 mtr within range of WiFi router | Within 300-400 meter within range of Rf | Within 700-1000 meter within range of Zigbee signals | Limited to the length of wire |
| Power supply | Required | Required | Not required | Not Required | Mostly Not Required |
| Battery back up | Available | Available | Available | Available | Mostly Not Available |
| Battle Life | Couple of weeks | Couple of weeks | Couple of Months Upto 1 Year | Couple of Months Upto 1 Year | Not Applicable |
| Most Suited for | Multiple rooms, server room | Refrigerators, rooms, server room | Open Warehouses | Open Warehouses | Multiple Rooms |
How to select a real time monitoring system?
While selecting a system for your requirements, consider the following questions before your decision making:
What are the parameters (eg. Temperature, humidity, pressure etc.) you want to monitor for each asset? If you have different assets such as refrigerators, cold rooms, warehouses etc. you may have to list out the parameter to be monitored for each asset.
What is the type of communication you prefer viz., WiFi, Rf etc.? If you want flexibility to frequently relocate your assets such as lot of refrigerators, small freezers etc., you may choose WiFi, Rf or Zigbee mode of communication. Also if you have moving racks in a warehouse it is ideal to use WiFi, Rf or Zigbee.
If you have only fixed assets you can go for Ethernet or IP based systems which may work out to be economical.
What are the type of alerts you want viz. Email, SMS, voice call, local hooter etc.
The sensor should continue to function even in case of power failure or communication failure. Hence, the sensors should have its own memory store the data and should be able to transmit the data to the base station once power or communication is restored.
If generating alert is your priority, the alert system should continue to function even in the case of power failure, server failure or communication failure. This means that the alert system should be independent and should have a battery backup.
What is the accuracy required by you for each parameter? Eg. if you want an accuracy of 0.1 °C, you may have to select accordingly. A sensors with 0.5 °C accuracy will be cheaper than that of 0.1 °C.
Do you want to see the current readings in each sensor screen? There are sensors with and without displays. eg. In a warehouse where you are placing sensors in inaccessible areas, you may not want a sensor with a display. In such cases, you can go for sensors without display which will be cheaper. The readings will be seen in the base station or a computer connected to the base stations
-
What is the memory capacity of each sensor? A sensors with memory capacity of 8000 readings means that it will store 8000 readings at a time. This means that if readings is taken every minute, the memory will last for 8000 minutes which is almost 5.5 days. eg. If you are afraid of frequent power failure or server failure, you may prefer to go for sufficient memory capacity.
If you are following US standards, you may prefer to have 21 CFR Part 11 compliant devices. This means that the manufacturer of the device should have tested the devices, software etc. for compliance with 21 CFR Part 11.
Is there an annual fee for the system or is it a one-time package?
Is it easy to calibrate the sensors each year?
Do you have provision to give electric power for each sensor? In such case, you have to provide electric power plugs for each sensor. Most of the Ethernet and Wifi type of sensors require power. However there are POE (Power over Ethernet) type sensors also available, but may be without battery backup. Rf and Zigbee type sensors generally have a longer battery life and may not need individual power plugs
If the sensors are not connected to power, you may need to check whether the battery of the sensor and the base station are rechargeable type.
Also please check how long the battery lasts after each recharge.
For sensors without a power supply, the sensor should generate an alert when the battery charge goes down to critical levels.
It will be very easy if the software can be operated from a web browser instead of installing a software. In such case, you can check the current data from any computer using your user id and password. Also, if it is browser based you can check on your mobile phone as well.
If you are more technically inclined you may prefer to use a mobile based application and you may like to check whether the supplier has a mobile application.
You may use this evaluation sheet for evaluating different manufacturers while selecting a remote monitoring system.

Do you want to record the data from a truck / van in the same system?
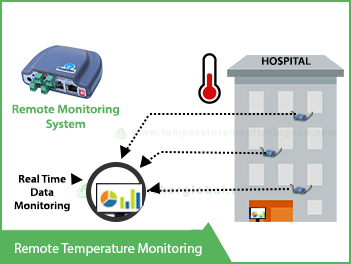
It is a common scenario that a customer will have a lot of trucks delivering goods from the warehouse and you may want to record the data from the truck. One option is definitely to use GPRS based real-time monitoring system. You may prefer to use a single set of software for your warehouse and the trucks.
An alternate option is to record the data inside the truck while it is out of your premises and transmit the data to your warehouse as soon as it comes back to the warehouse. In this case, you may not be able to monitor the temperature while the truck is on the move. But as soon as it reaches your premises it will automatically transmit data to your central system. This can be achieved through WiFi, Rf or Zigbee type of sensors. You can have a receiver (base station) in your loading/unloading area. One sensor will be installed in each vehicle. While the truck is within the range of the receiver, it will continuously transmit data to the receiver. However, as soon as the truck moves out of the premises the sensor starts recording in itself. When the truck reaches back to the warehouse it transmits all the recorded data automatically. This system will be much cheaper than a GPRS based system.
Further more details you can see videos in following links related.
Installation videos:
How to Configure Temperature and Humidity recording and Alert System Data Logger.
How to Configure IP Address of Temperature & Humidity monitoring System Data Logger
How to Calibrate the Sensors of Temperature & Humidity Monitoring System Data Logger
We Provide Following Solutions:

